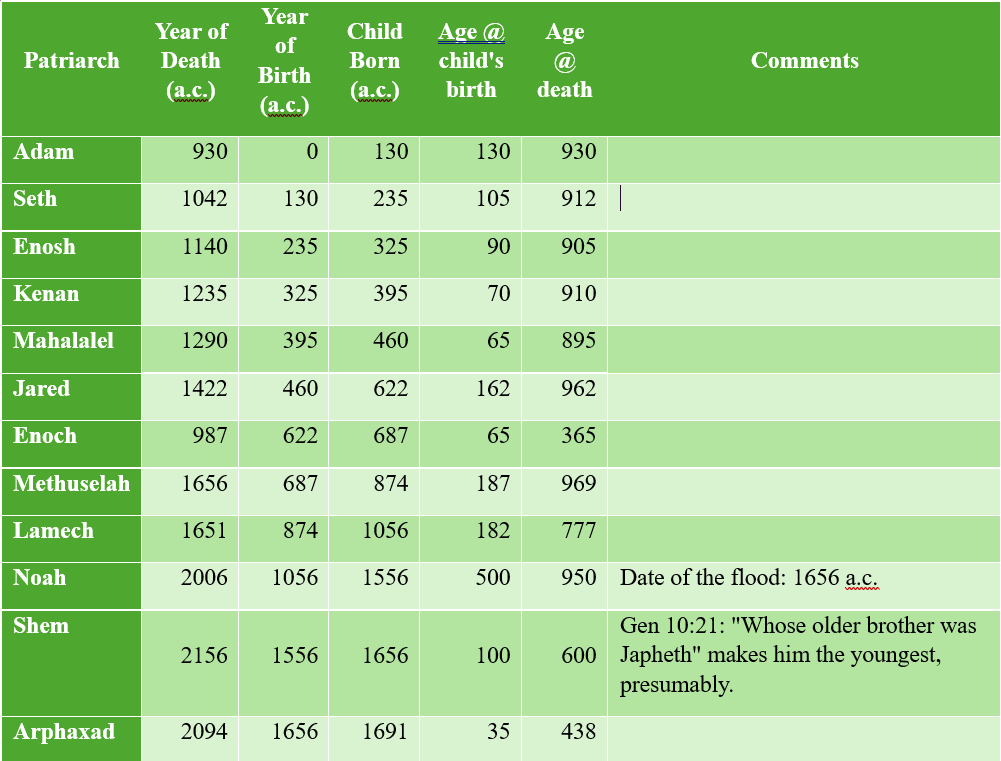
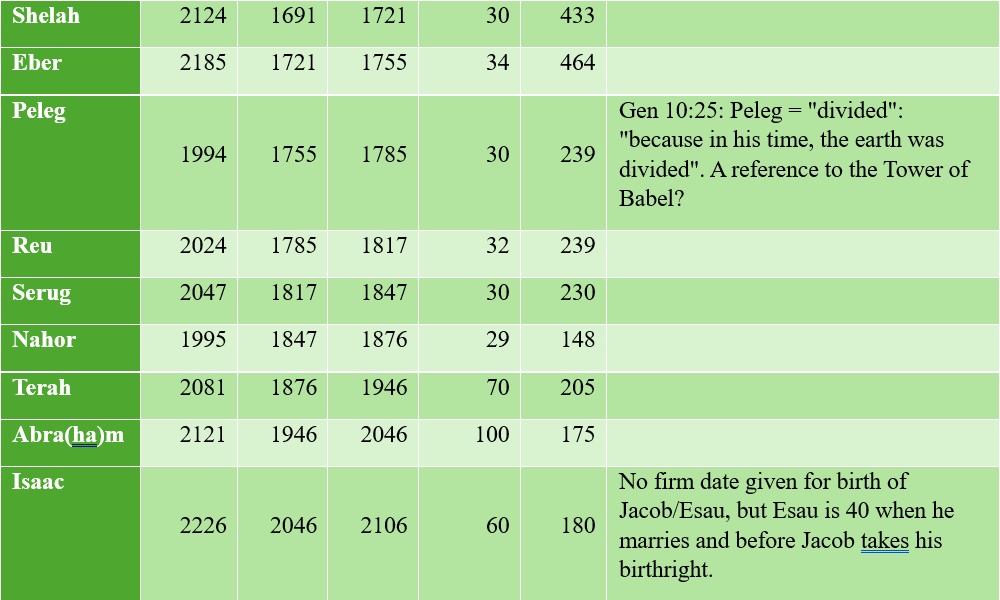
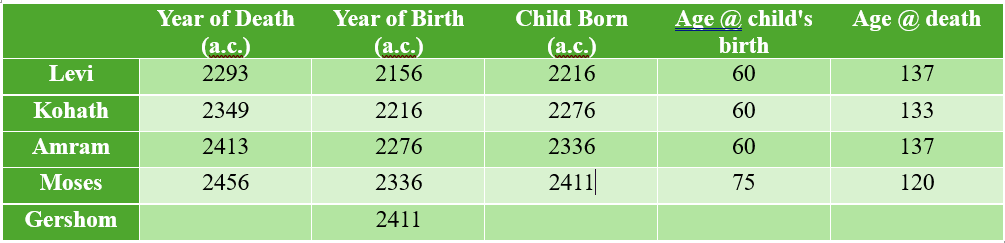
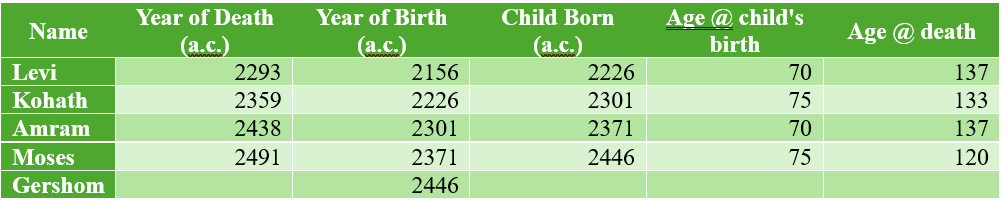
One of my favorite sections of Proverbs is 27:14–21. Here it is from the newest version of the NIV:
14 If anyone loudly blesses their neighbor early in the morning,
it will be taken as a curse.
15 A quarrelsome wife is like the dripping
of a leaky roof in a rainstorm;
16 restraining her is like restraining the wind
or grasping oil with the hand.
17 As iron sharpens iron,
so one person sharpens another.
18 The one who guards a fig tree will eat its fruit,
and whoever protects their master will be honored.
19 As water reflects the face,
so one’s life reflects the heart.
20 Death and Destruction are never satisfied,
and neither are human eyes.
21 The crucible for silver and the furnace for gold,
but people are tested by their praise.
Good Morning?
I’ve always been a morning person. I get up daily by 5:30 to get my Bible study in and get ready for work. But many years ago, when I came across Proverbs 27:14, I was in utter disbelief that such a verse would be in the Bible. Morning people are a curse to their neighbors! Now admittedly, I’m dealing with this a little tongue-in-cheek. I think most of us know what this verse is really talking about. You know the type, the one who sees you dragging into work before the coffee or other caffeinated beverage kicks in and decides to have a little fun at your expense. “Hi, Scott! Beautiful morning, isn’t it? Just breathe in that fresh morning air!” You want to turn around and smack the guy silly, right? Now of course, I’m not advocating that.
Keep in mind that Proverbs is not a book of commands, but a book of pithy generalities about life. They are statements that ring true to us about the way things are, but they were never intended to be transformed into commands. If you’re obnoxious early in the morning, some people just aren’t going to like that. In fact, the next two verses seem to have a similar theme: being obnoxious doesn’t win you any friends.
Good Wife?
The imagery Solomon applies to quarrelsome wives is even more striking. If you’ve ever had a leaky roof, you know exactly what he’s talking about. About a year ago, the same week I was moving out of my mom’s basement and into my own place, their upstairs toilet started leaking pretty bad into what had been my bedroom. It was a mess, to say the least, and a pain to keep up with. And trying to reason with a quarrelsome wife? Forget about it! Not only is it difficult to hold oil in your hand, but it’s also hard to get off unless you use some hot water and soap. Your hands feel slimy until you can get the oil off of them.
Good Men?
This brings me to Proverbs 27:17, a verse that is at the heart of nearly every men’s ministry message and program that’s ever been published. But as I’m prone to do, I’m about to shatter that long-held belief that the verse refers to positive male camaraderie. A look at the Hebrew of the verse and a little common sense about metallurgy will help make the point.
Have you ever watched someone forge a sword? First of all, you have to get the metal hot enough to melt into the basic shape of the sword. Then once the sword has its basic shape, it’s repeatedly subjected to the hot fire and hammered on an anvil to refine its shape and give it its edge. Once it has the length and temper it needs to be a good sword, the smith gives it its sharp edge by grinding and polishing. It is at that step of the process that we see the true nature of Proverbs 27:17.
When iron strikes iron, or even when iron sharpens iron, sparks fly. The Hebrew word for “sharpen” (חָדַד, ḥā∙ḏǎḏ) here is only used six times in the Old Testament: twice in Proverbs 27:17, three times in Ezekiel 21:9–11, and once in Habakkuk 1:8. Solomon’s use of the word in Proverbs 27:17 seems rather innocuous if we fail to look past the popular modern interpretation, but it is the second half of the verse that really got me thinking that this might not be the comfortable camaraderie often portrayed: “one man sharpens the face of a friend.” Now I ask you, does that sound like mutual encouragement? Does that sound like a slap on the back? NO! The passages in Ezekiel speak of the sword being sharpened for the slayer going out to slaughter. Habakkuk uses it to describe the fierceness of horsemen going out to battle. It sounds more like two guys battling each other just to stay ahead. It sounds like they might be getting on each other’s nerves. Granted, that could be for the better, but I think the context may suggest otherwise.
You still don’t believe me? An obnoxious morning person? A quarrelsome wife? She’s compared to oil, wind, a dripping faucet. But two men going at it? Iron on iron. Sparks are flying, baby. No holds barred. Hear the clank of hammer and steel on the anvil. Feel the crushing pain of missing the anvil and striking your thumb, times ten! And what about the verses that come after? Guarding, protecting: sounds like dangerous guy stuff. Death and Destruction never being satisfied: ’nuff said. Crucibles: subjected to the heat of purifying fire.
I think verse 19 is the crux verse here: “As water reflects the face, so one’s life reflects the heart.” I’ve been reading John Eldredge lately (Wild at Heart; Beautiful Outlaw), so I’m kind of pumped on guy stuff right now. I’m rediscovering what he calls the deep heart of a man: “a battle to fight, an adventure to live, and a beauty to rescue.” I’ve been asking myself what my life shows about my heart. Has it shown that I’m a warrior or a wimp? I’ve certainly picked my fights like William Wallace. They didn’t involve guns or swords, however. But they did often attack issues of the heart, especially greed and corruption. Those can be just as ugly as any battle scene from Braveheart. The trouble was, my “beauty” at the time didn’t want anything to do with my battle. That struck at the core of my manhood, and I’ve been climbing back ever since.
Guys, what does your life reflect about your heart? Are you the man’s man that Eldredge talks about in Wild at Heart? Or have you become a restrained Mr. Incredible, forced to keep your super powers in check behind an office desk because society is afraid of the inherent threat you pose to their comfort? If you haven’t read anything by John Eldredge, I would encourage you to get hold of a copy of Wild at Heart. The principles in there have taken me to a new level of manhood in my life, but I can still see that I have a long way to go. And if you’re in Omaha, beginning April 21, 2012, at StoneBridge Christian Church, 8:00 a.m., our men’s group will begin a nine-week series on Beautiful Outlaw.
Peace!
Scott Stocking
StoneBridge Christian Church is located at 15801 Butler Street, between Fort and Maple.